Case Quiz (June 2017)
A female patient, second child of nonrelated parents was born at 39 weeks’ gestation after a normal uncomplicated pregnancy and a normal spontaneous vaginal delivery. Her birth weight was 4.1 kg. She developed genu varum around age 1 year. Biochemical studies showed normal serum calcium, low serum phosphorus, significantly elevated alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels.
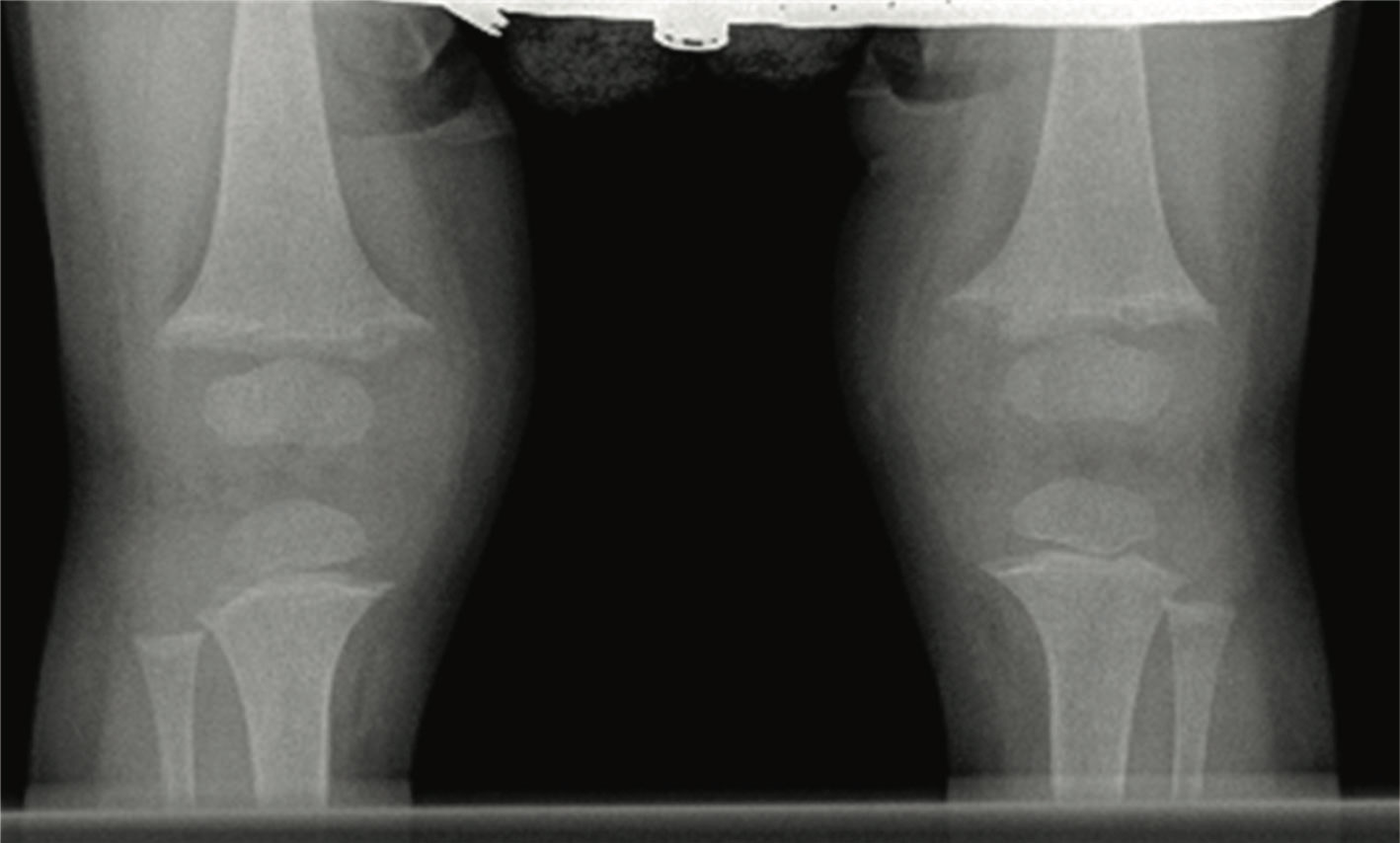
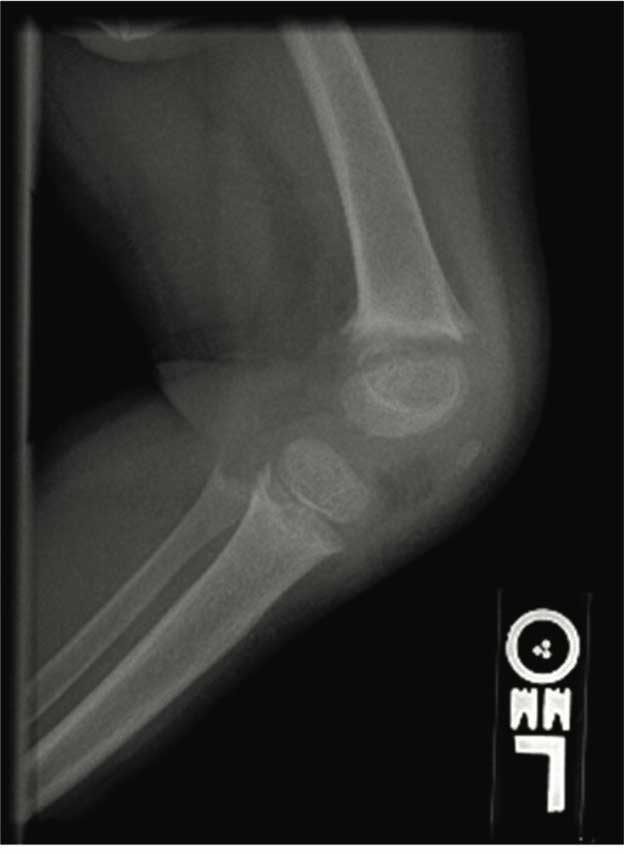
Radiographic studies of knee and wrist joints are showed in the upper figure. She was treated with ergocalciferol at various doses for 2 years with no improvement. Her serum 25 hydroxy vitamin D increased from 22 ng/mL at baseline to 80 ng/mL after a megadose of ergocalciferol. Repeat radiographs of her knees at age 3 years showed increased widening of epiphyses with increased cupping and fraying of the metaphyses (lower figure). She had complaints of polyuria, polydipsia, enuresis, and bone pain.
Further laboratory investigations at age 3 years revealed pH 7.29 with serum bicarbonate ranging from 19-20 mmol/L. Serum creatinine was normal at 0.4 mg/dL, Serum PTH level was normal. Renal ultrasound showed no nephrocalcinosis.
Case Answer (June 2017)
Our patient is likely to have Distal Renal Tubular Acidosis (DRTA) type I.
DRTA type I could happen due to nephrocalcinosis secondary to vitamin D intoxication